Bees sometimes make their way into homes while looking for a place to nest. The insects prefer dark and protected areas, so wall voids or chimneys often fit their needs. Any living space exposed to the outside is at risk for bee infestations.
Bees.com
- Bees are essential to our ecosystem because they pollinate plants and crops necessary for our survival. While fun and exciting, beekeeping with the right beekeeping equipment also helps increase the number of bees in our environment. The more beekeepers, the more healthy bees there are to pollinate and stimulate plant growth!
- Bee, (superfamily Apoidea), any of more than 20,000 species of insects in the suborder Apocrita (order Hymenoptera), including the familiar honeybee (Apis) and bumblebee (Bombus and Psithyrus) as well as thousands more wasplike and flylike bees. Adults range in size from about 2 mm to 4 cm (about 0.08–1.6 inches).
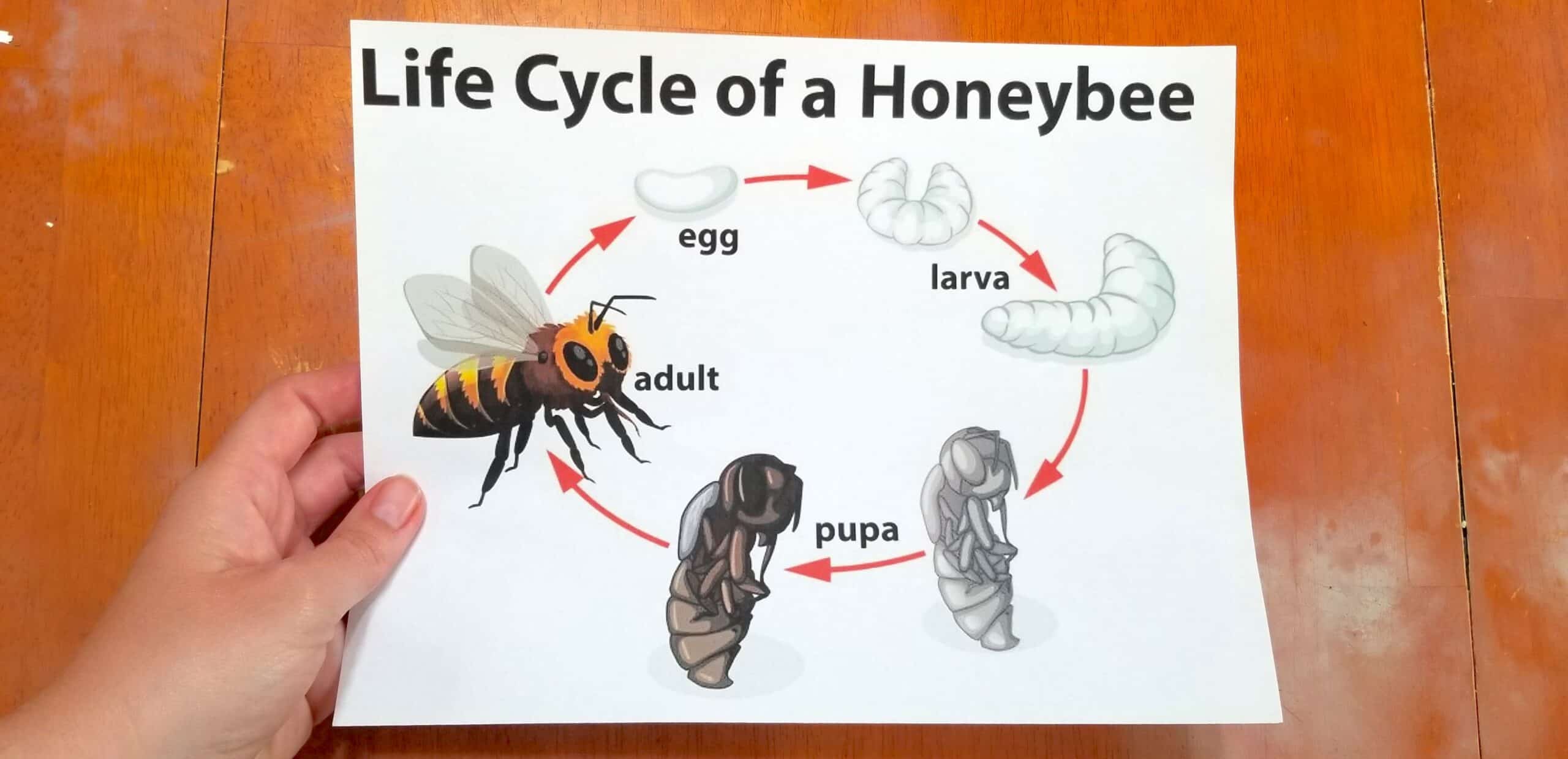
- Honeybee, (tribe Apini), also spelled honey bee, any of a group of insects in the family Apidae (order Hymenoptera) that in a broad sense includes all bees that make honey. In a stricter sense, honeybee applies to any one of seven members of the genus Apis —and usually only the single species, Apis mellifera, the domestic honeybee.
- Welcome to the LCBA website! This is the official website for the Lane County Beekeepers Association, a non-profit organization dedicated to the field of bees and beekeeping.
Characteristics
Bees are dependent on pollen as a protein source and on flower nectar or oils as an energy source. Adult females collect pollen primarily to feed their larvae. The pollen they inevitably lose in going from flower to flower is important to plants because some pollen lands on the pistils (reproductive structures) of other flowers of the same species, resulting in cross-pollination. Bees are, in fact, the most important pollinating insects, and their interdependence with plants makes them an excellent example of the type of symbiosis known as mutualism, an association between unlike organisms that is beneficial to both parties.
Bees Take-out Menu
Most bees have specialized branched or feathery body hairs that help in the collection of pollen. Female bees, like many other hymenopterans, have a defensive sting. Some bees produce honey from flower nectar. Honey bees and stingless bees commonly hoard large quantities of honey-a characteristic that is exploited by beekeepers, who harvest the honey for human consumption.
Olive Garden
Larry Crowhurst/Oxford Scientific Films
Bees.com Menu
There are about 20,000 species of bees worldwide. Some species may not yet have been discovered, and many are either not named or have not been well studied. Bees are found throughout the world except at the highest altitudes, in polar regions, and on some small oceanic islands. The greatest diversity of bee species is found in warm, arid or semiarid areas, especially in the American Southwest and Mexico. Bees range in size from tiny species only 2 mm (0.08 in) in length to rather large insects up to 4 cm (1.6 in) long. Many bees are black or gray, but others are bright yellow, red, or metallic green or blue.Social Structure and Nesting Habits
Bees have diverse nesting and social habits. This diversity has provided scientists with a natural laboratory for the study of evolution and social behavior in insects.
Texas Roadhouse
Solitary Bees
The primitive bees, like their relatives the wasps, are solitary. Each female makes her own burrow, in which she constructs earthen chambers to contain her young. She deposits pollen moistened with nectar or oil into individual cells until enough food has accumulated to provide for the young bee from egg hatching until the larva reaches full size. She then lays an egg on the pollen mass and seals the cell before going on to construct another cell.
